Why didn't My Airbag Go Off in a Collision?
There are certain types of accidents in which the air bag would not be expected to provide additional protection. These include rear impacts, second or third collisions in multiple impact accidents, as well as low speed impacts. Damage to the vehicle indicates a collision energy absorption, and is not an indicator of whether or not an air bag should have inflated.
To reduce the risk of an air bag deploying unexpectedly and causing serious injury or death:
-
Do not hit or allow any objects to impact the locations where air bags or sensors are installed.
-
Do not perform maintenance on or around the air bag sensors. If the location or angle of the sensors is altered, the air bags may deploy when they should not or may not deploy when they should.
-
Installing bumper guards with non-genuine Hyundai or non-equivalent parts may adversely affect the collision and airbag deployment performance.
To ensure correct function of the airbag system, have the bumper replaced with genuine Hyundai part or the equivalent (of the genuine part) specified for your vehicle.
-
Press the Start/Stop button to the OFF or ACC position and wait for 3 minutes when the vehicle is being towed to prevent inadvertent air bag deployment.
-
Have all air bag repairs conducted by an authorized HYUNDAI dealer.
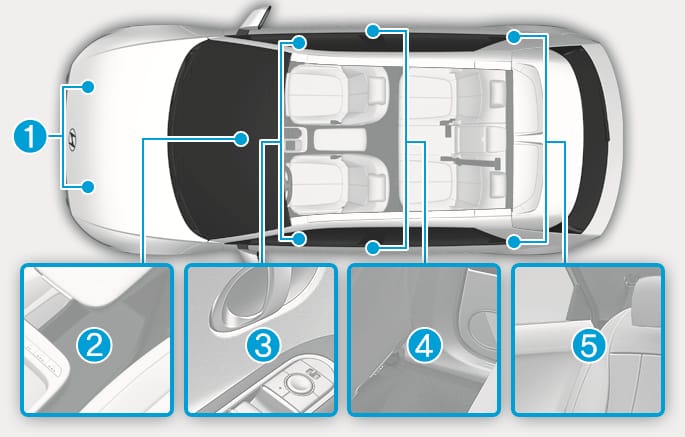
2C_AirbagSensorOverview
- Front impact sensor
- SRS control module/Rollover sensor
- Side impact sensor (Pressure)
- Side impact sensor (Acceleration)
- Side impact sensor (Acceleration)
Front air bags
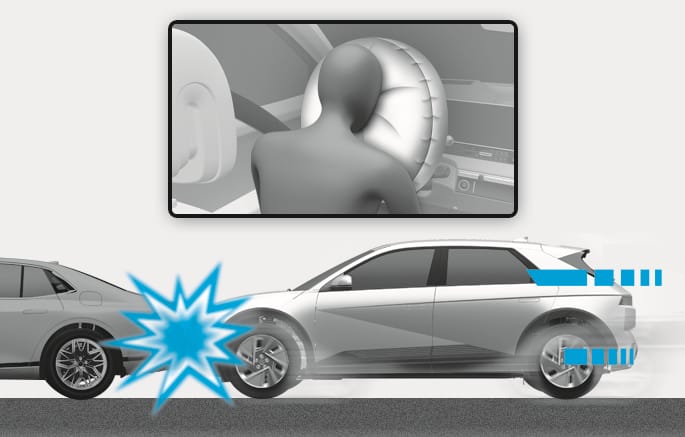
2C_AirbagOperatingConditionFrontAirbag
Front air bags are designed to inflate in a frontal collision depending on the severity of impact of the front collision.
Side and curtain air bags
2C_AirbagOperatingConditionSideAirbag
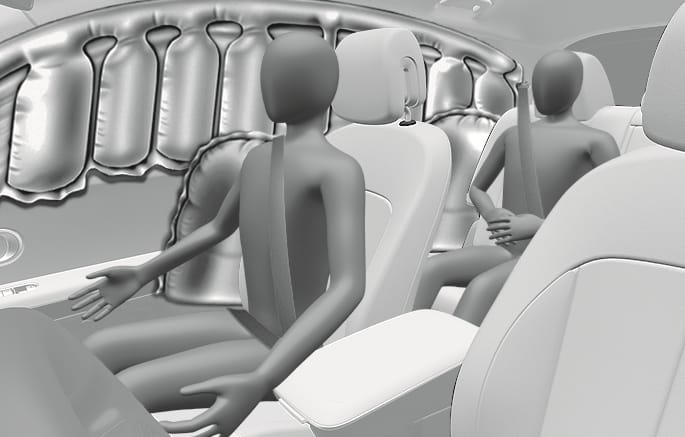

2C_SideCurtainAirbagDeployment
Side and curtain air bags are designed to inflate when an impact is detected by side collision sensors depending on the severity of impact resulting from a side impact collision.
Although the driver’s and front passenger’s air bags are designed to inflate in frontal collisions, they also may inflate in other types of collisions if the front impact sensors detect a sufficient impact. Side and curtain air bags are designed to inflate in side impact collisions, but they may inflate in other collisions if the side impact sensors detect a sufficient impact.
Also, the side and curtain air bags are designed to inflate when a rollover is detected by a rollover sensor.
If the vehicle chassis is impacted by bumps or objects on unimproved roads, the air bags may deploy. Drive carefully on unimproved roads or on surfaces not designed for vehicle traffic to prevent unintended air bag deployment.
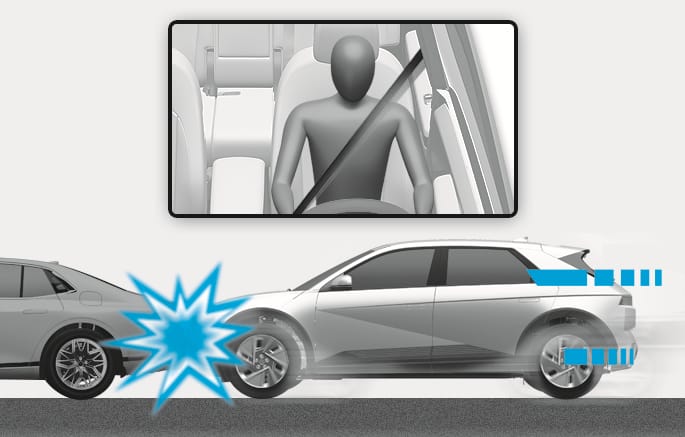

2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionMinorCrash
In certain low-speed collisions the air bags may not deploy. The air bags are designed not to deploy in such cases because they may not provide benefits beyond the protection of the seat belts.
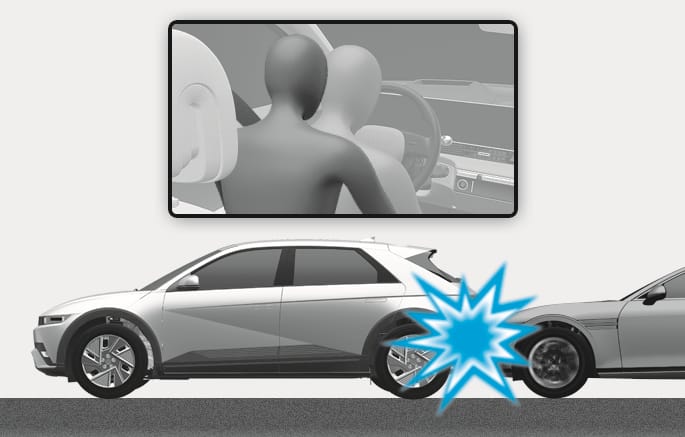
2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionRearCrash
Front air bags are not designed to inflate in rear collisions, because occupants are moved backward by the force of the impact. In this case, inflated air bags would not provide any additional benefit.
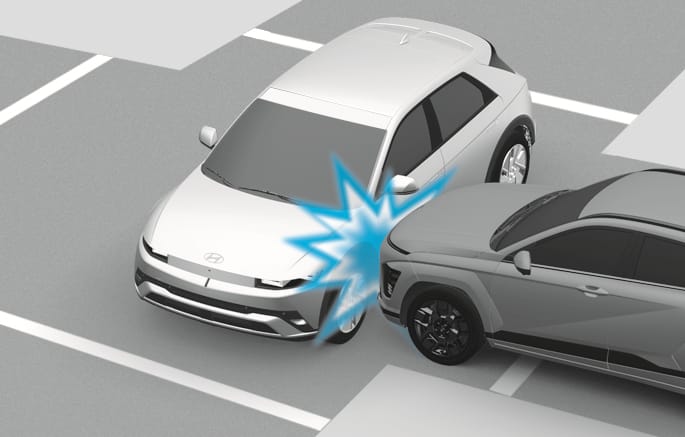
2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionSideCrash
Front air bags may not inflate in side impact collisions, because occupants move in the direction of the collision, and thus in side impacts, front air bag deployment would not provide additional occupant protection.
However, side and curtain air bags may inflate depending on the severity of impact.
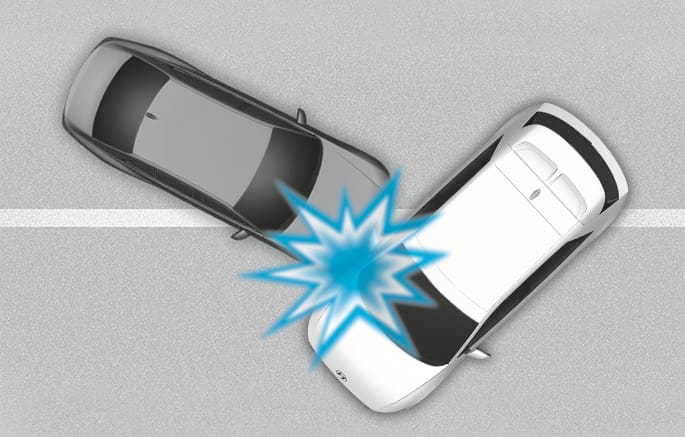
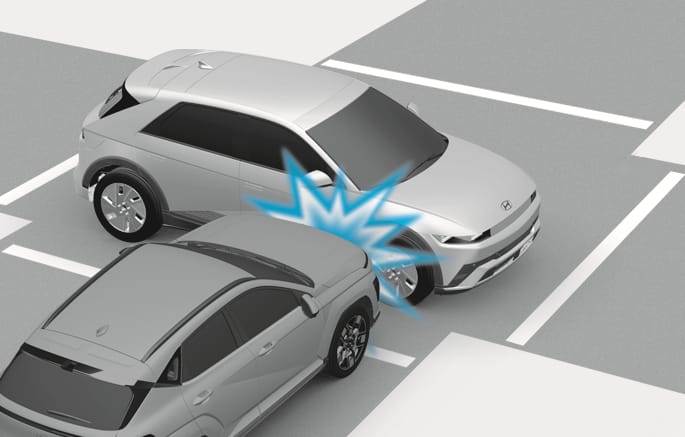
2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionSidlingCrash
In an angled collision, the force of impact may direct the occupants in a direction where the air bags would not be able to provide any additional benefit, and thus the sensors may not deploy any air bags.
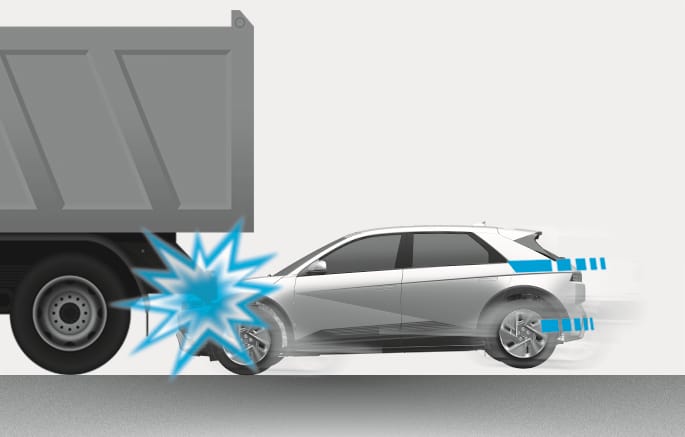
2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionTruckCrash
Just before impact, drivers often brake heavily. Such heavy braking lowers the front portion of the vehicle causing it to “ride” under a vehicle with a higher ground clearance. Air bags may not inflate in this “underride” situation because deceleration forces that are detected by sensors may be significantly reduced by such “underride” collisions.
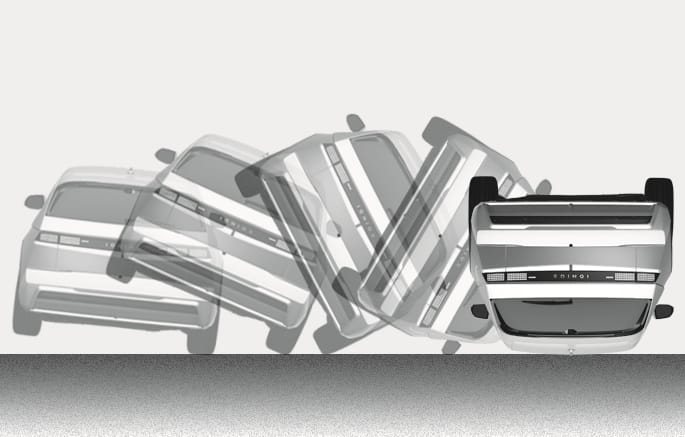

2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionTurnoverCrash
Front air bags may not inflate in rollover accidents because front air bag deployment would not provide additional occupant protection.
The side and curtain air bags may inflate in a rollover situation, when it is detected by the rollover sensor.
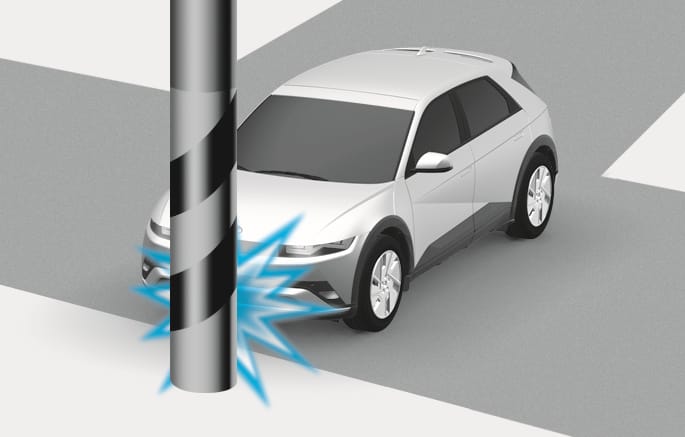

2C_AirbagNonOperatingConditionPollCrash
Air bags may not inflate if the vehicle collides with objects such as utility poles or trees, where the point of impact is concentrated and the collision energy is absorbed by the vehicle structure.